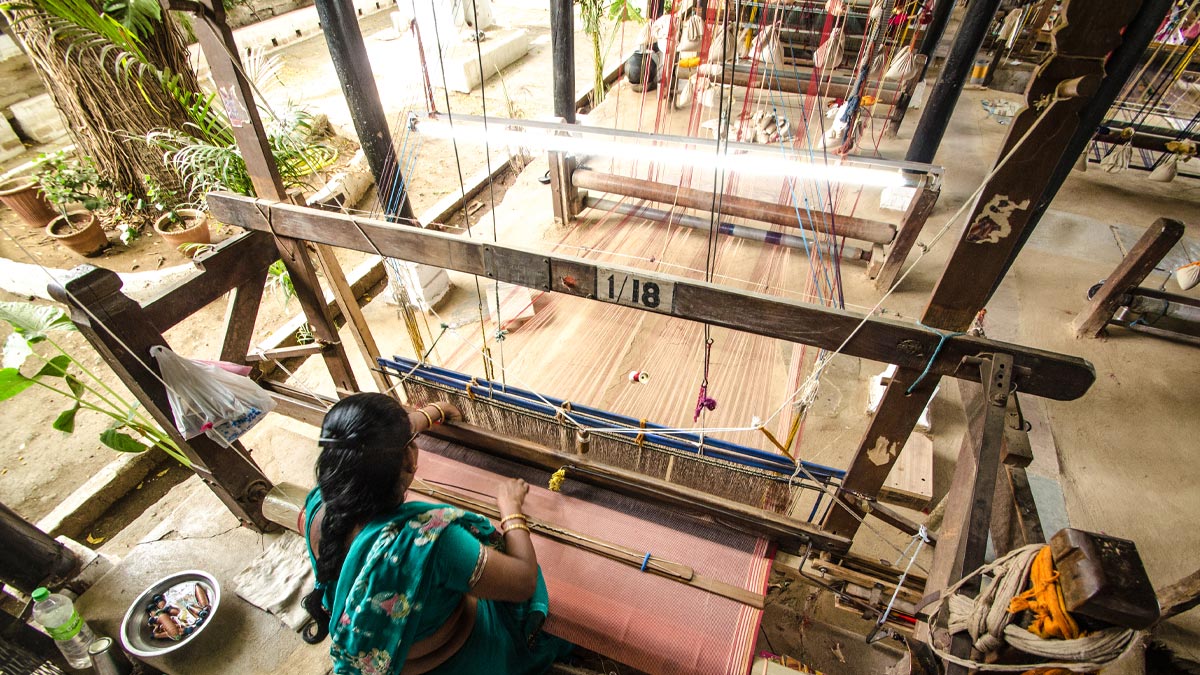
Rural India has a variety of industrial set-up including cottage industry, single-unit manufacturing, small and medium enterprises among others, since long-back. The traditional industries still thrive and provide employment to many villagers and people in the nearby areas. There are several traditional industries which are viably operative. These include handloom, handicrafts, coir, cashew, beedi, tiles and bricks and other household industrial activities carried out in the rural parts of the country. Traditional industries are labour intensive, relying on skills passed on from one generation to another generation. Mostly these industries comes under the category of Micro, Small and Medium enterprises (MSMEs)
The MSMEs contribute about 30 per cent to India’s GDP In terms of exports as well, they are an integral part of the supply chain and contribute about 40% of the overall exports. MSMEs also play an important role in employment generation, as they employ about 110 million people across the country. Governments at various levels, time and again, have implemented various schemes in order to protect and promote rural entrepreneurship and traditional industries. Here are some the schemes imitated by the government for their development –
Prime Minister's Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP)
Launched by the centre in 2008, this scheme is a credit-linked subsidy programme undertaken to generate self-employment opportunities through establishment of micro-enterprises in the non-farm sector and providing help to traditional artisans and unemployed youth. The scheme is implemented by Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) functioning as the nodal agency at the national level. At the State level, the scheme is implemented through State KVIC Directorates, State Khadi and Village Industries Boards (KVIBs), District Industries Centres (DICs) and banks.
A Scheme for Promoting Innovation, Rural Industry & Entrepreneurship (ASPIRE)
This scheme was launched in 2019 to create new jobs and reduce unemployment, promote entrepreneurship culture in India, boost grassroots economic development at the district level, facilitate innovative business solutions, and promote innovation to further strengthen the competitiveness of the MSME sector. The scheme helps by providing for incubation and commercialisation of Business Ideas Programme through technical/research institutes, including those in the field of agro-based industry. These would be designated as Knowledge Partners and would incubate new/existing technologies for their commercialisation.
Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries (SFURTI)
The scheme aims for the development of khadi, village industries, and coir clusters by providing them with improved equipment, common facilities centres, business development services, training, capacity building and design, and marketing support, etc. The scheme invites applications from non-government organisations (NGOs), institutions of the Central and State governments and semi-government institutions, field functionaries of State and Central government, Panchayati Raj institutions (PRIs), private sector bodies by forming cluster-specific special purpose vehicles/entities (SPVs), corporate, and corporate social responsibility (CSR) foundations with expertise to undertake cluster development.
Credit Guarantee Scheme for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE)
It facilitates credit to MSMEs through collateral-free credit facility (term loan and/or working capital) extended by eligible lending institutions to new and existing micro and small enterprises. The MSME Ministry and Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) jointly established a Trust named Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises in order to implement Credit Guarantee Scheme for Micro and Small Enterprises. 75 per cent of the loan amount to the bank is guaranteed by the Trust Fund. It provides collateral-free loan up to a limit of Rs 100 Lakh for individual MSMEs on payment of a guarantee fee to the bank.
Credit Linked Capital Subsidy Scheme (CLCSS)
It facilitates technological development of small scale industries, including khadi, village and coir industrial units, by providing 15 per cent upfront capital subsidy with a upper limit of Rs 15 Lakh. Its objective is to upgrade the plant and machinery of small enterprises with state-of-the-art technology, with or without expansion, and also for new MSMEs, which have set up their facilities with appropriate, eligible and proven technology duly approved under scheme guidelines.
Apart from these, the government have certain other schemes aimed towards the development and conservation of the traditional industries in India. It also aims to keep the spirit of entrepreneurship alive and going in the rural area.